White Paper
Presentation
Tutorials/Demonstrations
I. Audio Frequency Synthesizer
- Open GNURadio
- Double click “Options” Block
- Change QT GUI to WX GUI
- Click the Magnifying Glass to search
- Type “Signal Source”
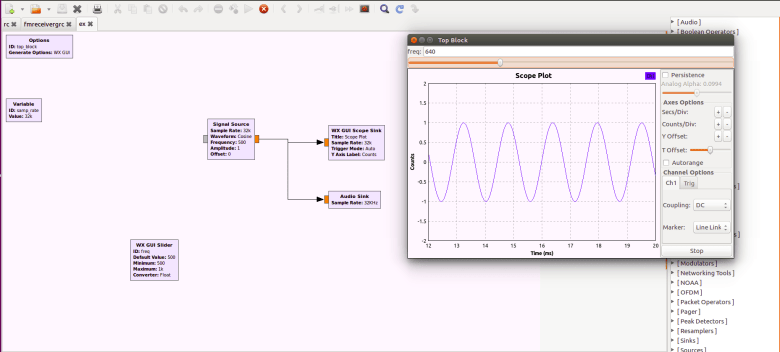
- Double Click “Signal Source”
- You should now have a signal source block
- Search for and double click “WX Scope Sink”
- Search for and double click “Audio Sink”
- Connect the output of Signal Source to Scope Sink
- Connect the output of Signal Source to Audio Sink
- Ensure Variable samp_rate block, Signal Source Sample Rate, Scope Sink Sample Rate, and Audio Sink Sample Rate are all set to 32kHz
- Search and double click “WX GUI Slider”
- Set Slider ID to “freq”
- Set Slider default value to 500
- Set Slider Min value to 500
- Set Slider Max value to 1000
- Set Signal Source Sink to “freq”
- Compile and Run (press green play button)
- Save
- You should see the scope and the frequency should play out of your speakers. You can change frequency with the slider above the scope
II. FM Receiver with HackRF One
- Open GNURadio
- Double click “Options” Block
- Change QT GUI to WX GUI
- Double Click “Variable” samp_rate block
- Set Value to 2e6
- Click the Magnifying Glass to search
- Type “osmocom Source”
- Double Click “osmocom Source”
- You should now have an osmocom source block
- Set osmocom source frequency to freq. Make sure output is complex
- Search and double click “WX GUI Slider”
- Set ID to “freq”. Set default to 100e6. Set min to 90e6, set max to 105e6
- Search and double click “Rational Resampler”
- Set Interpolation to 1 and Decimation to 4. Make sure input and output are complex
- Wire output of osmocom Source to input of Rational Resampler
- Search and double click “Low Pass Filter”
- Set Decimation to 1, Gain to 1, Cutoff Frequency to 100k, and Transition Width to 1e6. Make sure input and output are complex
- Wire output of Rational Resampler to Low Pass Filter
- Search and double click “WBFM Receive”
- Set quadrature rate to 500k, Audio Decimation to 10. Make sure input is complex and output is float
- Wire Low Pass Filter to WBFM Receive
- Search and double click “Rational Resampler”
- Set Interpolation to 48 and Decimation to 50. Make sure input and output are float
- Wire WBFM Receive to Rational Resampler
- Search and double click “Multiply Const”
- Set constant to “vol” and make sure input and output are float
- Wire Rational Resampler to Multiply Constant
- Search and double click “Audio Sink”
- Set Audio Sink sample rate to 48kHz
- Wire Multiply Const to Audio Sink
- Search and double click “WX GUI Slider”
- Set default value to 0.5, set min to 0, set max to 1
- Search and Double click “WX GUI FFT Sink”
- Wire output of osmocom source to FFT Sink
- Compile and Run
You should see a spectrum analyzer plot and two sliders. One slider controls volume and the other controls frequency. Slide the volume to max and make sure your computer speakers are enabled. Slide the frequency to areas of the spectrum analyzer with peaks until you find a radio station that you can hear clearly.

III. Reverse Engineering an RC Car Controller
The first half of this tutorial (up to but not including transmission) will work for reverse engineering devices that us ASK, FSK, and PSK as their modulation scheme but the example used in this tutorial is for ASK (which is the most common modulation scheme for cheap remote control cars and other cheap wireless devices).
- Look for the FCC ID of the device that you want to reverse engineer. Often these are located in the battery cover.
- Go to FCCID.io and type in the FCC ID. Here you will find important information including carrier frequency and modulation scheme. If you cannot find the FCC ID, you can still continue with this tutorial
- Open GNURadio
- Double click the “Options” Block and change QT GUI to WX GUI
- Double click the “Variable” Block samp_rate and change its value to 2e6
- Search and double click “osmocom Source”
- Set osmocom Source frequency to the frequncy found using th FCC ID (Note: If you could not find the FCC ID, use the osmocom source with a sliding frequency like in tutorials I and II and wire the osmocom source to an FFT block. You can slide around while enabling the wireless device you are trying to reverse engineer to look for peaks within the frequency range you believe it to be within)
- Wire the osmocom source to a scope and an FFT block (Don’t forget to make sure that the variable types agree)
- Compile and Run
- Transmit using the device you are trying to reverse engineer and ensure that you are observing the correct frequency
- Search and double click a “Complex to Float”
- Wire the output of the osmocom source to the type converter
- Search and double click “Wav File Sink”
- Select a file name and location in the Wav File Sink block and wire the real output of the type converter to the input of Wav File Sink
- Open and view your wav file (using a program like Audacity)
- Here, you must use some visual analysis. Review the concepts of ASK, FSK, and PSK and see if you can see any of those modulation schemes. If you do, you should be able to extract the bitstream. You should also be able to determine the bit period by observing the length of each bit. See example image at the end of the tutorial
- Create a new GNURadio file
- Set samp_rate to 2e6 and switch from QT GUI to WX GUI
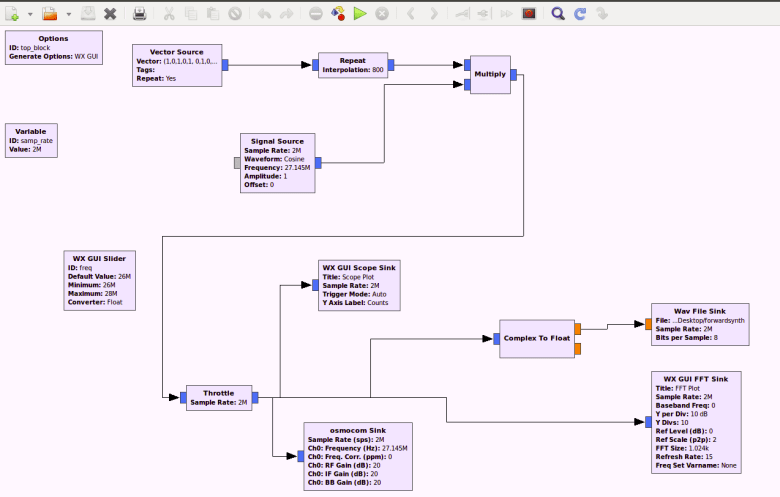
- Search and double click “Vector Source”
- Change the vector in the Vector Source to the bitstream found in Step 16 (Example: 1101 –> (1,1,0,1))
- Search and double click “Repeat”
- Set Interpolation to (sample rate) times (bit period) (Note: you should be able to visually determine the bit period from step 16)
- Wire the Vector Source to the Repeat block
- Search and double click “Signal Source”
- Set frequency to the frequency found initially
- Search and double click “Multiply”
- Wire the Repeat block and the Signal Source to the inputs of the multiplication block (Ensure the inputs and outputs of the multiply block are set to complex)
- Search and double click “Throttle”
- Set Throttle to 2e6
- Wire Multiply to Throttle
- Search and double click “WX GUI Scope”
- Wire Throttle to scope
- Repeat steps 31 and 32 for WX GUI FFT Sink
- Search and double click “Complex to Float”
- Wire Throttle to type converter
- Search and double click “osmocom Sink”
- Set osmocom Sink frequency to the frequency found earlier
- Wire Throttle to osmocom Sink
- Compile and Run
Here is an example for an RC Car being controlled using ASK Modulation at 27.145MHz
Received wave opened in Audacity:

Signal being “on and off” indicates ASK and the repetitions indicate a single command being repeated several times
Zoomed In:
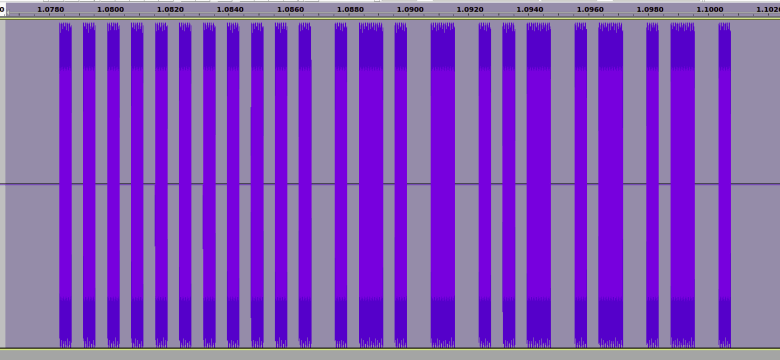
This indicates a bitstream of:
10101010101010101010100101101001100101011001011001011001
And a bit period of 0.4mS
Transmitter Flowgraph: